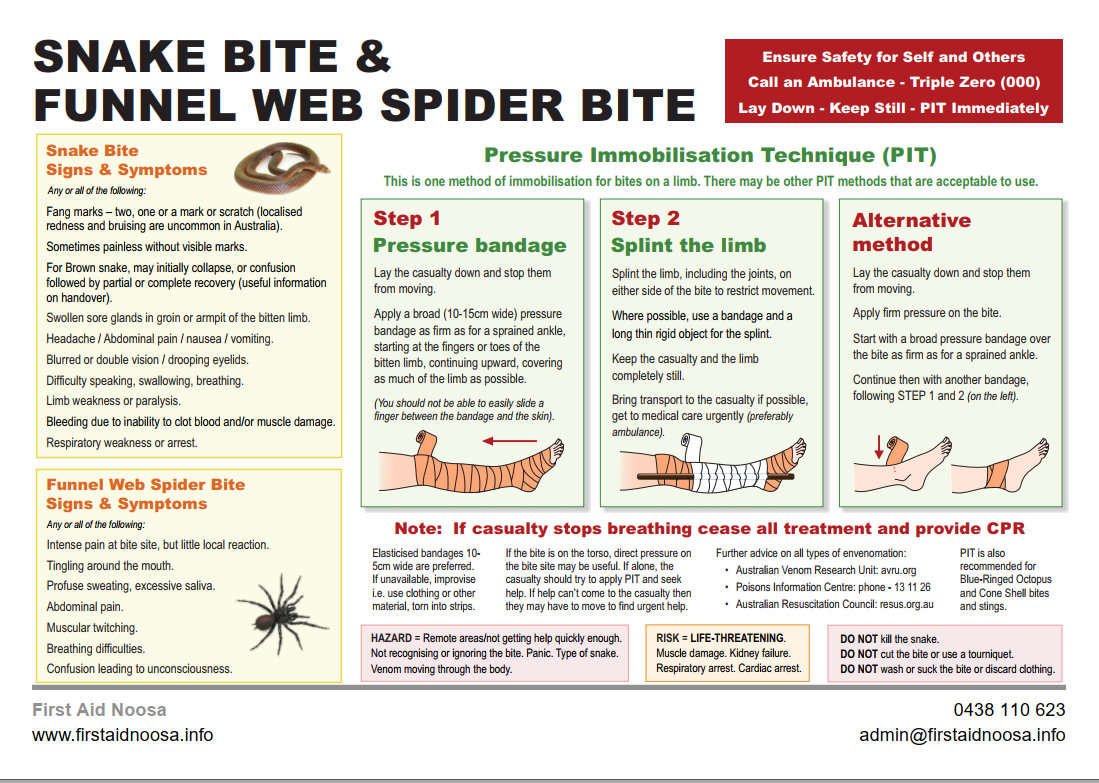
Snake Bite
Many snakes in Australia are capable of lethal bites. These include: taipans, brown snakes, tiger snakes, death adders, black snakes, copperhead snakes, rough scaled snakes and many sea snakes. Anti-venom is available for all venomous Australian snake bites.
Snake identification – Identification can be made from venom on clothing or the skin using a Venom Detection Kit. Do not wash or suck the bite or discard clothing. Do not kill the snake for identification purposes, you may get bitten yourself and medical services do not rely on visual identification of the snake species.
Signs and symptoms
Two fang marks, however only a single mark or a scratch may be present (localised redness and bruising are uncommon in Australian snake bite)
The bite may sometimes be painless and without visible marks
Headache
Nausea and vomiting
Occasionally, initial collapse or confusion followed by partial or complete recovery
Abdominal pain
Blurred or double vision, or drooping eyelids
Difficulty speaking, swallowing or breathing
Swollen tender glands in groin or axilla of the bitten limb
Limb weakness or paralysis
Respiratory weakness or respiratory arrest
First aid
Treat immediately, life-threatening effects may be seen in children within minutes
Lie the casualty down, keep him/her still and provide reassurance
Apply a pressure immobilisation bandage using pit
If the bite is not on a limb, firm direct pressure over the bite site may be useful
Transport the casualty to the hospital preferably by ambulance